Scroll down to bottom for Video Library and Resources

Course Description:
AP World History is an advanced placement course designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of global history from approximately 1200 CE to the present. This course emphasizes the interconnectedness of societies and civilizations, exploring major events, developments, and trends that have shaped the modern world. Students will engage in critical analysis of historical sources, develop historical arguments, and examine the complexities of historical processes and their impacts on contemporary issues.
The course is organized into thematic units that cover key concepts, including human societies and cultures, political structures, economic systems, social interactions, and technological innovations. Students will explore diverse perspectives and engage in comparative analysis to understand how different societies have influenced and been influenced by one another.
Course Objectives:
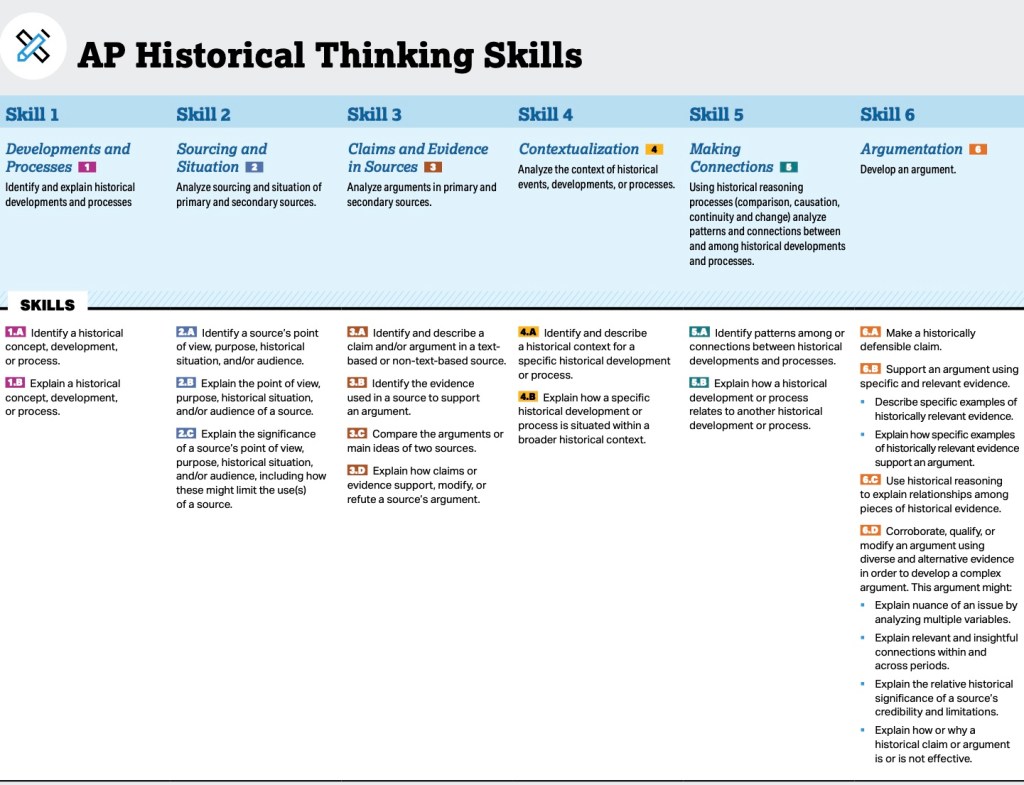
- Historical Thinking Skills: Develop and refine skills in historical analysis, including chronological reasoning, comparison, contextualization, and causation. Students will learn to evaluate primary and secondary sources, construct historical arguments, and use evidence to support their conclusions.
- Understanding Historical Themes: Examine and interpret key historical themes such as the development of civilizations, political and social structures, economic systems, and cultural exchanges. Analyze how these themes have evolved and intersected across different regions and time periods.
- Global Connections: Explore the interconnectedness of world regions and how interactions among societies—through trade, migration, conflict, and diplomacy—have influenced global history. Investigate the impact of these connections on political, economic, and cultural developments.
- Diverse Perspectives: Analyze historical events and processes from multiple perspectives, including those of different social classes, genders, ethnicities, and regions. Understand the role of individual and collective agency in shaping historical outcomes.
- Historical Interpretation: Evaluate and critique various interpretations of historical events and trends. Understand how historians use evidence to construct narratives and how these interpretations can change over time based on new evidence or perspectives.
- Preparation for the AP Exam: Prepare for the AP World History exam through targeted practice in multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and essay writing. Develop strategies for time management, critical thinking, and effective communication of historical arguments.
By the end of the course, students will have a deep and nuanced understanding of world history and be well-prepared to engage with historical questions on a higher level.
General Information About AP World: Unit Breakdown and Reasoning Processes
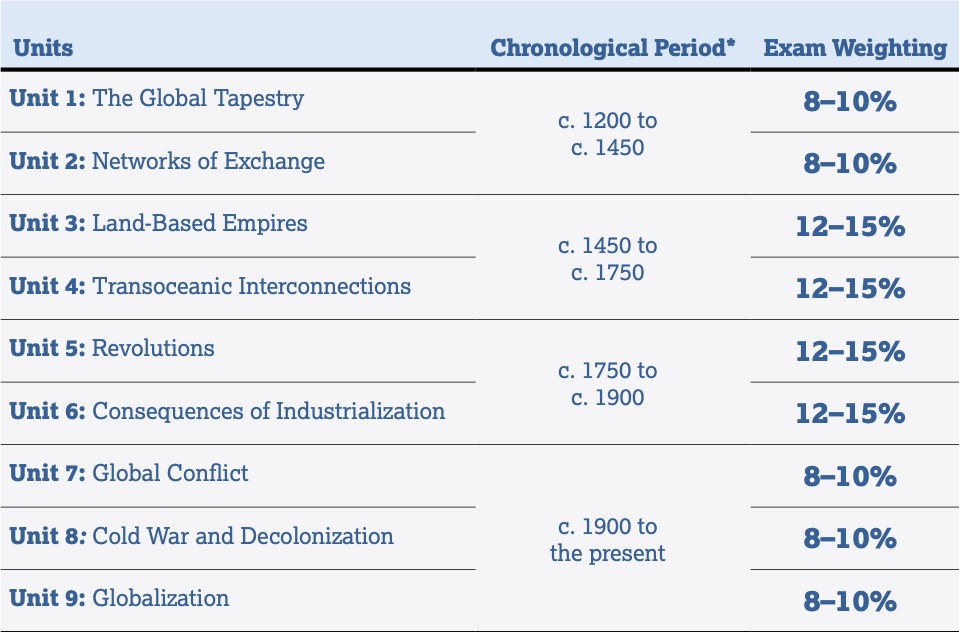
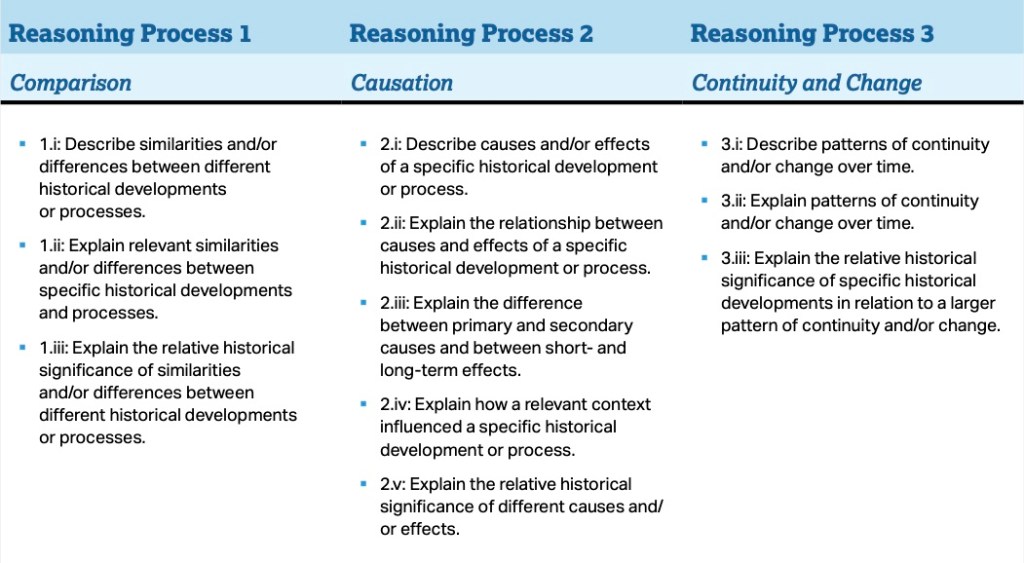
Reasoning processes are critical to understand because all your questions and essays are going to center around one of these themes.
Resources:
Video Library:
5 Essentials for Unit 3: Land Based Empires
Proudly powered by WordPress
